|
5. TAXONOMIES II and III
|
A. Rules governing STEMS only
5.1 – Stems with bullet points
|
Bullet points are used when a stem contains numerous and/or complex information (equipment and/or conditions). This way, the information is more legible and referenced quickly and easily.
-
The stem begins with ‘Given the following information:’.
-
The bullets begin with a capital (upper‑case) letter.
-
The order of elements in a bullet is ‘information: measurement’.
-
The bullets have no final punctuation, since they are used to give brief information in phrase form, not in complete sentences.
-
All or most of the information is contained in the bullets.
-
The interrogative sentence is placed at the end of the stem, after the bullet points, with more information added for context, if required. This allows the candidate to take in the necessary information before processing it.
|
|
Incorrect examples
|
Correct examples
|
-
A 140 kPa (20 psig) gas system has 38 mm (1 1/2 in) welded piping and a total developed length of 50.3 m (165 ft.). What is the procedure to test the gas system?
|
-
Given the following information:
-
Gas system: 140 kPa (20 sig)
-
Welded piping: 40 mm (1 1/2 in.)
-
Total developed length: 50 m (165 ft.)
What is the procedure to test the gas system?
|
-
Given the following information:
-
Channel equals 305 mm (12 in.).
-
Height = 381 mm (15 in.)
-
Length is 762 mm (30 in.).
What is the weight of 24 roof rafters if each rafter weighs 38.7 kg/m (26 lb./ft.)?
|
-
Given the following information:
-
Channel: 305 mm (12 in.)
-
Height: 381 mm (15 in.)
-
Length: 762 mm (30 in.)
-
Weight of 1 rafter: 38.7 kg/m (26 lb./ft.)
What is the weight of 24 roof rafters?
|
-
Refer to Figure 136. Given the following information, what is the procedure to test the gas system?
-
140 kPa (20 psig) gas system
-
38 mm (1 1/2 in.) welded piping
-
50.3 m (165 ft.) total developed length
|
-
Refer to Figure 136. Given the following information:
-
Gas system: 140 kPa (20 psig)
-
Welded piping: 38 mm (1 1/2 in.)
-
Total developed length: 50.3 m (165 ft.)
What is the procedure to test the gas system?
|
|
NOTE:
|
Bullet points are allowed in a diagram item.
|
|
5.1.1 – Colon
|
In bulleted lists, there is 1 space after the colon.
|
|
Incorrect example
|
Correct example
|
-
Refer to Figure 84. Given the following information:
-
Boom length=80 ft.
-
Boom angle is 45.7°
|
-
Refer to Figure 84. Given the following information:
-
Boom length: 80 ft.
-
Boom angle: 45.7°
|
5.2 – Multiple statements + question
|
Placing the interrogative sentence at the end of the stem allows the candidate to take in the necessary information before processing it.
|
NOTE:
|
It is best practice to write short sentences. Try to break up longer sentences where possible.
|
|
|
Incorrect Taxonomy II example
|
Correct Taxonomy II example
|
-
In a boiler room that has appliances with draft control devices, the combustion air supply is located low to the floor, while the ventilation air supply is located at maximum height. What is the purpose of the arrangement?
|
-
A boiler room contains appliances with draft control devices. The combustion air supply is located low to the floor. The ventilation air supply is located at maximum height. What is the purpose of the arrangement?
|
|
Incorrect Taxonomy III example
|
Correct Taxonomy III example
|
-
An engine equipped with a DPF has excessive regeneration, and the ECM shows a fault code indicating low combustion temperature. What is the cause?
|
-
An engine is equipped with a DPF. There is excessive regeneration. The ECM shows a fault code indicating low combustion temperature. What is the cause?
|
5.3 – Diagrams
|
When developing an item that is or will be linked to a diagram, there is no need to manually type ‘Refer to Figure X.’ in the stem’s text box. When a diagram is linked to an item in ICEMS, this phrase is automatically inserted at the beginning of the stem.
|
|
B. Rules governing both STEMS and RESPONSES
5.4 – What is the procedure vs What is done
5.4.1 – What is the procedure
|
When all 4 responses in an item contain 2 or more sequential actions, the item is developed in the following manner:
-
the stem asks ‘What is the procedure to’;
-
the last action in each response is preceded by a comma and ‘then’.
|
|
Correct examples
|
|
-
What is the procedure to replace a flex line on a gas appliance?
-
Apply gas tape, then tighten flare nut on flex nut.
-
Secure union, then tighten flare nut on flex line.
-
Apply pipe dope, then tighten flare nut on flex line.
-
Tighten union, then secure flare nut on flex line.
|
-
What is the procedure to apply a 4 ft. strip of SBS base sheet?
-
Chalk a line, imbed granules, position sheet, then torch.
-
Prime curb, chalk a line, embed granules, then torch.
-
Chalk a line, position sheet, embed granules, then torch.
-
Prime curb, position sheet, chalk a line, then torch.
|
5.4.2 – What is done
|
The stem must ask ‘What is done to’ in the following instances:
-
all responses contain only 1 action;
-
2 responses contain only 1 action and 2 responses contain 2 or more actions (either sequential or non sequential);
-
2 of the 4 responses contain at least 2 actions – non sequential (i.e. contain ‘and’ rather than ‘then’).
|
|
Correct examples
|
-
After lengthening a wheelbase, a unit displays poor steering control. What is done?
|
|
A. Change steering arms.
|
|
B. Adjust steering gear free play.
|
|
C. Adjust drag link, then offset for road crown.
|
|
D. Change steering arms, then adjust toe setting.
|
|
|
🠘 1 action
|
|
🠘 1 action
|
|
🠘 2 actions
|
|
🠘 2 actions
|
|
-
During installation, what is done to maintain the alignment of open web steel joists?
|
|
A. Adjust turnbuckles.
|
|
B. Install cables
|
|
C. Test bridging and adjust bushing wear.
|
|
D. Apply tension and grease sag rods.
|
|
|
🠘 1 action
|
|
🠘 1 action
|
|
🠘 2 actions
|
|
🠘 2 actions
|
|
5.4.2.1 – What is done — Avoid creating a Taxonomy I item
|
When asking ‘What is done’, the responses must avoid:
-
repeating the same verb at the beginning of each response, as this often "disguises" an actual Taxonomy I ‘What is it?’ item;
-
using synonyms of a verb (e.g. check / verify / determine / observe / look at), as this often "disguises" an actual Taxonomy I ‘What is it?’ item.
|
|
Incorrect examples
|
Correct examples
|
-
Locking tapered hubs are removed from a drive line assembly. What is done?
-
Use hammer and punch to shock hubs apart.
-
Use puller to separate hubs.
-
Use heat to loosen hubs.
-
Use jackscrews to separate hubs.
|
-
Locking tapered hubs are removed from a drive line assembly. What is done?
-
Shock hubs apart with hammer.
-
Detach hubs with puller.
-
Loosen hubs with heat.
-
Separate hubs with jackscrews.
|
-
What is done to determine the freshness of an egg?
-
Verify colour of yolk.
-
Determine size of yolk.
-
Find out spread of white.
-
Check odour of egg.
|
-
What is done to determine the freshness of an egg?
-
Run finger along egg shell.
-
Measure size of yolk.
-
Tap egg shell.
-
Smell yolk.
|
5.5 – Dimensions
|
Dimensions are expressed with the multiplication symbol ‘×’, not the lower‑case letter ‘x’, and are kept together using non-break spaces.
|
|
Incorrect examples
|
Correct examples
|
-
Steel plates measure 1.27 cm x 1.22 m x 2.44 m (1/2 in. x
4 ft. x 8 ft.).
|
-
Steel plates measure 1.27 cm × 1.22 m × 2.44 m (1/2 in. × 4 ft. × 8 ft.).
|
-
-
Install a glass pane measuring no more than 5 ft. 11
3/4 in. x 9 ft. 11 1/2 in.
|
-
-
Install a glass pane measuring no more than 5 ft. 11 3/4 in. × 9 ft. 11 1/2 in.
|
|
|
5.6 – Diagrams
|
Only Taxonomy II and III items refer to diagrams. Items with diagrams are most often Taxonomy II. However, when a diagram item also includes complex calculations, then the items are classified as Taxonomy III. Refer to 3.1 – Rules governing Taxonomy III stems only.
|
|
NOTE:
|
Items linked to diagrams depicting basic symbols, such as warning labels and hand signals, are classified as Taxonomy II. Even though a diagram may be very basic or simple, the candidate is required to perform an action by referring to the exam booklet to determine the correct response.
|
|
5.6.1 – Terminology and spelling
|
It is best practice that the terminology and spelling used in a diagram be reproduced in the item it is linked to for the sake of consistency. In case of discrepancy, it is preferable to use the diagram spelling. When trade experts object to a term or spelling in a diagram, the term or spelling can be changed by making a request to the Host and ESDC Advisor during a workshop.
|
|
NOTE:
|
When there is disagreement with the terminology provided in the RSOS, seek consensus among all workshop participants and provide the correction and rationale to the RSOS Team Lead if modifications to the RSOS are required.
|
|
5.6.2 – Units of measurement and symbols
|
In an item linked to a diagram, the responses always use the unit of measurement and never the symbol, even when the diagram itself uses symbols. This is done to avoid legibility issues. For example, the symbols for inch / second (") and foot / minute (') are easy to misread.
|
|
Incorrect example
|
Correct example
|
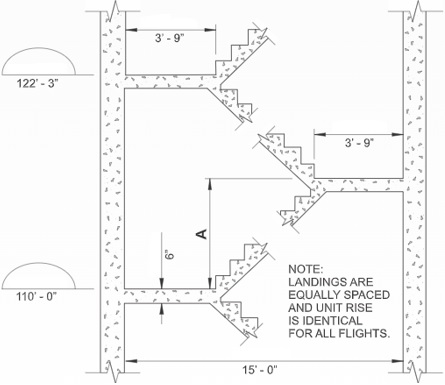
FIGURE 22
|
-
Refer to Figure 22. 30' ‑ 6" is to be added to the height of the building. Unit rise is required to remain identical for all flights. What is the dimension of A?
-
9' ‑ 9 3/16"
-
9' ‑ 10 3/8"
-
10' ‑ 1 1/16"
-
10' ‑ 2 7/8"
|
-
Refer to Figure 22. 30 ft 6 in. is to be added to the height of the building. Unit rise is required to remain identical for all flights. What is the dimension of A?
-
9 ft. 9 3/16 in.
-
9 ft. 10 3/8 in.
-
10 ft. 1 1/16 in.
-
10 ft. 2 7/8 in.
|
|
Incorrect example
|
Correct example
|
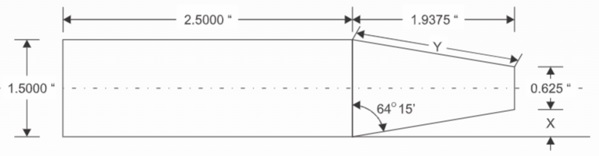
FIGURE 15
|
-
Refer to Figure 15. What is the included angle of the taper?
-
6°, 21', 14"
-
12°, 43', 27"
-
25°, 26', 55"
-
50°, 53', 50"
|
-
Refer to Figure 15. What is the included angle of the taper?
-
6°, 21 min, 14 s
-
12°, 43 min, 27 s
-
25°, 26 min, 55 s
-
50°, 53 min, 50 s
|
5.7 – Codebook measurements
|
Codebook questions use the measurement system, imperial or metric, used in that codebook.
|
|
Correct examples
|
|
-
Given the following information:
-
Building size: 9.6 m × 14 m
[...]
What is the minimum size built‑up floor beam required?
-
4‑ply 38 mm × 235 mm beam.
-
4‑ply 38 mm × 286 mm beam.
-
5‑ply 38 mm × 235 mm beam.
-
5‑ply 38 mm × 286 mm beam.
|
-
A 10 ft. length of 4 in. water‑filled pipe is being hung. The pipe weighs 8 lb./ft. What is the minimum weight requirement at each support?
-
80 lb.
-
325 lb.
-
400 lb.
-
650 lb.
This item is linked to Sprinkler Fitter, National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) 13 – 2016 codebook: 9.1.1.2 (1) – Imperial only.
|
|
This item is linked to Carpenter, National Building Code of Canada – 2015: Table 9.23.4.2 – Metric only.
|
|
|
C. Rules governing RESPONSES only
5.8 – Responses with 2 or more actions
|
Only Taxonomy II and III items include responses with 2 or more actions.
|
5.8.1 – Avoid combining 2 steps into 1 step
|
Two (2) distinct steps must not be combined into 1 single step – not even to arrange the length of a response to be more balanced with the other responses.
|
|
Incorrect examples
|
Correct examples
|
-
-
Check wind direction and strength, then adjust boom.
|
-
-
Check wind direction, check wind strength, then adjust boom.
|
In this example, the first step is divided into 2 sequential steps to clarify the order in which they must be done.
|
-
-
Configure current to DCSP and AC, then set pressure.
|
-
-
Configure current to AC, configure current to DCSP, then set pressure.
|
In this example, not only must the first step be divided into 2 steps, but the sequence of steps is wrong and must be reversed.
|
-
-
Cut and clean pipe ends, then join pipes.
|
-
-
Cut pipes, clean pipe ends, then join pipes.
|
In this example, the first step is divided into 2 sequential steps because it contains 2 distinct actions.
|
-
-
Measure, then lay out and grease joists.
|
-
-
Measure joists, lay out joists, then grease joists.
|
In this example, ‘joists’ is the object of all 3 verbs and the last step (with ‘then’) contains 2 actions which may not be sequential. As a result, the response must be divided into 3 steps and specify the correct sequence.
|
5.8.2 – Commas in procedures
|
Only commas are used to separate non-final steps in a procedure, not semi‑colons.
|
|
Incorrect example
|
Correct example
|
-
What is the procedure to remove a damaged SRS control module?
-
Unbolt module; disconnect wires; remove lock pin; then remove module.
|
-
What is the procedure to remove a damaged SRS control module?
-
Unbolt module, disconnect wires, remove lock pin, then remove module.
|
5.8.3 – Sequential actions — Then
|
When the actions must be performed in a specific order, the final action is preceded by a comma and ‘then’.
|
|
Correct example
|
|
-
-
Remove interior panel, release clips, then cut adhesive.
|
|
5.8.4 – Non-sequential actions — And
|
When the actions can be performed in any order, the final action is preceded by ‘and’ with no Oxford comma.
|
|
Correct example
|
|
-
-
Size tank to task, ensure access and secure heat source.
|
|
5.8.4.1 – Oxford comma before final and — Exception
|
The Oxford comma precedes the final ‘and’ when:
-
another ‘and’ precedes it;
-
its omission may result in ambiguity;
-
there is no sequence involved.
|
|
Correct examples
|
|
-
-
Check block and tackle, and verify crane reach.
|
-
-
Sausages, fish and chips, and tartar sauce.
|
|
NOTE:
|
Reversing the clauses above eliminates the comma altogether.
-
Verify crane reach and check block and tackle.
|
|
|
5.9 – Sequential lists — Numbers and letters
|
When a sequential list of numbers or letters are the entirety of a response, the response ends in a period. The final number or letter is not preceded by a comma and ‘then’.
|
|
Correct examples
|
|
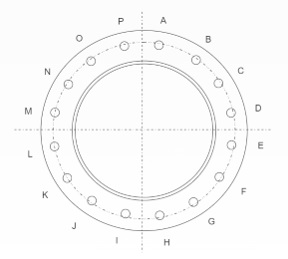
FIGURE 99
|
-
What is the serving order for the prepared courses?
-
Cooked omelet
-
Grilled 1 in. steak rare
-
Grilled 1 in. steak well done
-
Barbecue wings with cilantro
-
New York‑style strawberry shortcake
-
Martini with olive
-
Poached 1 in. salmon steak
-
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7.
-
6, 7, 1, 2, 4, 2, 5.
-
2, 4, 7, 1, 3, 5, 6.
-
6, 3, 2, 1, 4, 7, 5.
|
-
Refer to Figure 99. What is the torque sequence on a 16‑bolt maintenance hole cover?
-
P, A, B, C.
-
P, C, K, F.
-
P, D, H, L.
-
P, H, D, L.
|
|
NOTE:
|
A descending order of responses may be considered if an exam contains recurring correct answer patterns among the items in a block or MWA – e.g. several items, all with responses in ascending order and whose correct answer key is noticed to be nearly all the same
|
|
5.10 – Diagram designations
5.10.1 – Single characters
|
Objects in diagrams may include a 1‑character designation. In these cases, responses do not require a period at the end. Refer to 4.34.1 – Final period.
|
|
Correct examples
|
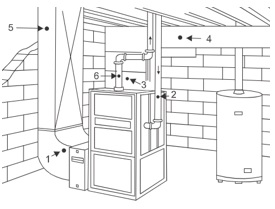
FIGURE 44
|
-
Refer to Figure 44. Where are air samples taken?
-
1
-
2
-
3
-
4
|
|
-
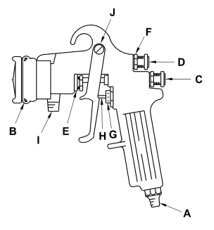
Refer to Figure 55. The sprayer has been used for spraying car door frames. When spraying a car roof, which part is adjusted to change the fan spray pattern?
-
C
-
D
-
F
-
J
|
FIGURE 55
|
5.10.2 – Multiple characters
|
Objects in diagrams may include a multiple‑character designation.
|
5.10.2.1 – Multiple letters
|
Responses with multiple‑letter designations are written in alphabetical order and do not require a period. Refer to 4.34.1 – Final period.
|
|
Correct example
|
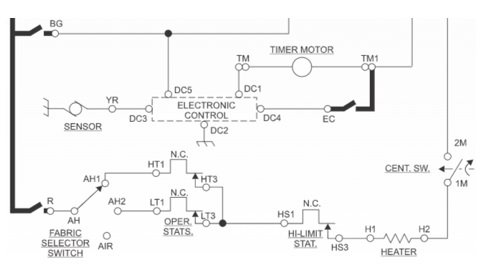
FIGURE 2
|
-
Refer to Figure 2. The timed cycle for cool down is always too long. Where is the problem located?
-
BG
-
EC
-
TM
-
YR
|
|
5.10.2.2 – Alphanumeric
|
Responses with alphanumeric designations are written in alphabetical order and do not require a period. Refer to 4.34.1 – Final period.
|
|
Correct example
|
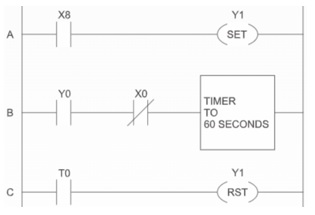
FIGURE 31
|
-
Refer to Figure 31. Which address on line B activates the timer?
-
T0
-
X0
-
X8
-
Y0
|
|
|
|






